| LEARN
FLAT RAFT STEP BY STEP |
| |
INTRO & LIMITATIONS +
EXCERPTS FROM IS : 2950 - PART 1 - 1981 |
|
|
 |
Please take Print
Out of Every Step, including this page before commencing Learn.
Take a Yellow Marker Pen
and Mark the Learning Process while Proceeding further.
This is Essential for Learning. |
 |
The software
performs Analysis, Design, Estimation, Costing & AutoCAD Drawing of RCC
Rigid Flat Raft Foundation.
The Software
basically requires a User to enter Raft data for Joints, Columns, Beams, Slabs & Continuity. The rest of the things are taken care of by the
software.
The results are displayed in the form of BM & SF, Raft Hidden Beam & Slab Schedule,
Quantities, Cost & Approximate Bar bending Schedule for Beams.
Graphics option are available for display and tabular Format is available for
Editing and Deleting Data.
A User should Delete / Edit Input-Data through the
various Program Options only. If any editing is done
outside the design environment than Data files may become corrupted. All
Data should be Strictly
"Entered" as explained in following steps.
Extensive Printing options are available under each
display.
Printing is straight forward with default set of values ( Arial Font, 8 mm
Thick, Bold, Portrait ).
Only
Beam Schedule will be Printed in Landscape
Orientation.
The best way to go about the software is to Mark on the Foundation Plan, Joint, Beam,
Column and Slab Numbers. A Joint represents a Column location or an intersection
between 2 Raft Beams. The Beams are represented by its location in the form of Right
Hand Side (RHS) & Left Hand Side (LHS) Joint numbers. The Slabs are represented
by LEFT BOTTOM & RIGHT TOP joint numbers. All Joints will have X & Y
Co-Ordinates, Top Left corner is taken as origin (0, 0). Joint / Beam / Column /
Slab numbers should start with " 1 " and should not be repeated.
The Program will generate automatic Joint, Beam, Column & Slab Numbers from the
information given in Project File. Some of these Numbers / Members may not be
required & shall be deleted in a systematic manner as explained in the following
chapters. The Final Plan Graphics should look exactly as the Raft Foundation Plan. |
 |
Cantilever Raft beams
/ Slabs cannot be analyzed. |
 |
Beams / Columns /
Slabs shall be along two mutually perpendicular axis
(X and Y). Polygonal
(Multi-sided) slabs cannot be analyzed. |
 |
 |
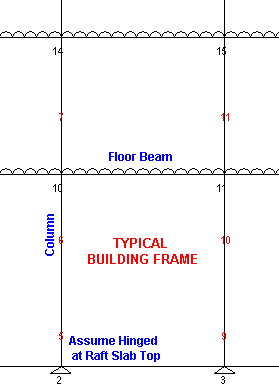
Analyze the Structure, assuming Raft Top
(Column Base) as Hinged
(Refer Graphics above). Hence there shall be no Moments on Raft Top.
Structure shall be Analyzed in Either direction. Hence User shall enter 3
Column Load Cases, i.e.
● DL + LL
● DL + LL + Wind / Seismic Load in Ton (From X-X Direction)
● DL + LL + Wind / Seismic Load in Ton (From
Y-Y Direction)
End Column Reactions on Raft Beams (DL + LL + Wind or Seismic) are obtained by running 2-D or 3-D
Frame
Analysis programs separately.
User may use our 2-D
Frame Analysis software for calculation of End Reactions.
|
 |
Export to Excel :
When the " Analysis Result -> Bending Moment & Reaction " option is Run, a Text
file is automatically created. This File will open in Any Text Editor. You can
also Open this Text File in EXCEL.
Start Excel -> File -> Open -> Delimited ->Next : Delimiters -> Comma ->Next ->
Finish.
Now you will notice that Complete Data is displayed in Excel Spread Sheet.
If more than One File is Created, Corresponding to Each of Load Cases, than Open
Excel Sheet for Each File (Load Case). In Excel Sheet Editing, Deleting,
Sorting, Printing & Merging of Data/Files/Excel Sheets is Extremely Easy. This
way any no. of Load Cases can be Manipulated.
Similar Text files are created in " Shear Corrected BM & SF " (Design BM & SF),
" Raft Beam Schedule " and " Raft Slab Schedule option for Exporting
Results to Excel Spread Sheet & its subsequent Manipulation.
|
 |
Intersecting Joints
between two Beams (Main & Secondary) is assumed as Hinged. Hence no Moment
transfer is envisaged. |
 |
Connection between
End Column and Beam is considered as Hinged. Hence no Moment transfer is
envisaged between Column and Beam. |
 |
After data input, the user has
to switch over to graphic option for visual checking of joints / columns / beams
/ slab nos. When the data is error free the user can run the Analysis,
Design and Quantity options. The various results are also available through
display or print options. |
 |
Analysis, Design and Quantity
options should be run in strict order, else program will give unexpected
results. |
 |
Program creates
automatic Joint numbers as per nos. of Horizontal & Vertical Grids. Here Grids
means Beams coming along Column center lines as well as all Internal
Beams not aligned with columns. A user has to input Information regarding
Horizontal & Vertical Grids while creating Project File. |
 |
A user can delete
the Joints not required by using Joint Option. |
 |
Joints will be
automatically re-numbered when "UPDATE" button is clicked or at "EXIT". |
 |
Remember to Delete / Edit Corresponding Beam /
Column / Slab Member, whose Joint has been deleted. |
 |
Always delete Beam
/ Column / Slab member from the "END" to facilitate further Editing. After
Deleting press "UPDATE" button for re-numbering of members. |
 |
After Deleting
corresponding Beam / Column / Slab Member & Updating, edit the required Joint
Numbers of affected Beam / Column / Slab Members. |
 |
Go through the "READ
ME" Button for better understanding of that particular Option. |
 |
Raft Beam & Slab Design is as per IS
456 - 2000. Refer IS 2950 : Part 1 - 1981 / 1965 For Rigid
Raft Design / Relative Stiffness Factor. |
 |
Hidden Beam Depth < 200 mm not
permitted. |
 |
Beam Width >
8000 mm not permitted. |
 |
Links (Stirrups) < 75 MM for
Hidden Beams is not permitted. |
 |
Beam Reinforcement > 4 % not
permitted. |
 |
Age factor is
considered as 1.15. |
 |
For Durability aspect of
Design, refer our " Super Civil CD "
software. |
 |
All Columns are
placed Centrally with respect to Beams in either direction. There is no
provision to offset the column in either direction. If the offset is large than
user should re-workout the Beam Span. |
 |
Minimum Computer RAM memory
of 1 GB is recommended. |
 |
Use Laser OR Ink
Jet Printer. |
 |
References:
1. IS - 2950 - Part 1 -
1981.
2. BS - 8110 - 1997.
3. IS - 456- 2000 / 1978 / 1964.
4. SP 24 - 1983.
5. Advance Reinforced Concrete Design by P. C. Varghese.
6. Reinforced Concrete Designers Handbook by C. E. Reynolds.
|
| IMPORTANT
FEATURES OF FLAT RAFT |
 |
Hidden
Beam marking in flat Raft Slab is different than the normal Raft plan GA.
1: Mark the Hidden
Beams (Column
Strips) in the same way as you Mark the
Normal Beams but remember the following differences.
2: Hidden Beam (Column
Strips) depth shall
= Flat Raft (Middle
Strips) Thickness.
3: All Flat Raft Slab (Middle
Strips) thickness
shall be uniform.
4: Initial (Trial) Flat
Raft Slab Thickness =
Max.
Span of Beam or Slab in the Floor in MM ÷ 7.
5: Keep Column Size as
Large as Possible, Larger the Column size lesser
the Flat Raft Slab thickness.
6: Minimum Column size
allowed is 300 x 300 MM.
7: Try to Avoid
secondary beams, i.e. hidden beams resting on one another.
8: Concentrated loads
Loads are not Permitted.
9: Convert wall line load
in to UDL as w ÷ (0.6 * slab_span). and avoid beam
below wall line load. Refer IS 456-2000, clause
24.3.2.
10: Hence convert all
internal partitions in to equivalent UDL & avoid beams.
11: Try to Keep Minimum
spacing of beams at 2.0 M C/C.
12: In order to get most
optimum design keep the slab and beam spans
uniformly within 20 % of each other.
13: Spacing of columns
shall be as uniform as possible within say 20 % of each
other.
14: Avoid Eccentricity of
Walls vis a vis Hidden Beams and Columns.
15: One Way Shears are
calculated at effective depth from Column face and
Punching shear at deff ÷ 2.
16: BMs
are calculated at Column face.
BM
& SF are calculated at Beam Center Line for Beam to Beam Joint.
17: Raft Slab depth to be
revised, if steel area exceeds 245 cm2.
18: In Case of Un-safe
Hidden Beam design Reframe the Plan or Revise Slab
Depth or Column Size or Concrete Grade.
19: Flat Raft Slab Design is
meant for Vertical Loads only.
20: Main Steel is to be
placed in Longer Direction & not in Shorter Direction.
21: Convert Non
Rectangular Column into Equivalent Square Column
before Designing.
22: Min Reinforcement % in
Either Direction in Hidden beam = 0.20 %.
23: Reinforcement Spacing
Shall not Exceed 2 x Depth.
24: Use High Grade of
Concrete Preferably M 30 or M 35.
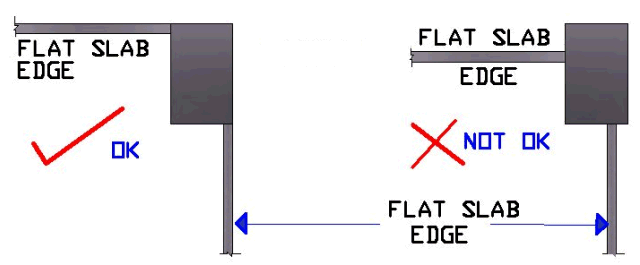
25: At Ends and Corners
the Flat Raft Slab shall Extend up to or beyond Outer
Edge of Column / Beam Else Flat Raft
Slab will Fail in
Punching.
Refer Details as under.
It is Preferable
to extend at least 300 MM beyond Beam / Column face.
26: Large openings cannot
be provided in Flat Raft Slab.
27: Small openings say
<= 300 MM can be located near the center of Slab.
28: Staircase / Lift Well panel shall
be treated as normal slab & not as opening,
Program will calculate the Loads
automatically.
29. In case of Unsafe Flat
Raft Slab / Hidden beam Design, any one or all of
the
following Corrective measures shall be adopted.
 Reframe General Arrangement (GA) / {Beam layout} Plan.
Reframe General Arrangement (GA) / {Beam layout} Plan.
 Revise Hidden Beam /
Flat Raft Slab thickness.
Revise Hidden Beam /
Flat Raft Slab thickness.
 Increase Column
Size.
Increase Column
Size.
 Increase Concrete
Grade.
Increase Concrete
Grade.
|
 |
Export to PDF:
A free PDF Creator Program is available with this Software. Designer can
directly export to PDF instead of printing various reports. |
|
|
| EXCERPTS
FROM IS : 2950 - PART 1 - 1981 |
 |
IS : 2950 - Part 1
is CP for Design & Construction of Raft Foundation. |
 |
In granular Soil,
the SBC of Raft is generally very high, however for rafts placed at
considerable depth (Like Basements) the punching mode of failure shall be
investigated. The Influence of soil compressibility & related scale
effects should be assessed.
For Rafts on cohesive soils, the stability against deep seated failures &
effect of long term settlement shall be taken in to consideration.
The Depth of Raft Foundation shall not be Less than 1.0 M. |
 |
Rigidity of
Foundation tends to iron out uneven deformations & thereby modifies the
contact pressure distribution. High order of rigidity is characterized by
large moments & relative small uniform settlements. A rigid Foundation may
also generate high secondary stresses in structural members. The effects of
Rigidity shall be taken in to account in the analysis. |
 |
Rigid foundation
design is based on the assumption of linear distribution of contact pressure.
The basic assumption of this method are :
(a) The Foundation is rigid relative to the supporting soil & the
compressible soil layer is relatively shallow.
(b) The contact pressure is assumed as planner, such that the centroid of the
contact pressure coincides with the line of action of the resultant force of
all loads acting on the foundation.
This method may be used when either of the following conditions is satisfied.
(a) The structures behaves as rigid (due to combine action of the
superstructure & the foundation) with a relative stiffness factor K >
0.50. (Refer Appendix C)
(b) The Column spacing is less than 1.75 / Ã. (Refer Appendix C)
The Raft is analyzed as a whole in of the two perpendicular direction &
analysis is based on statics.
|
|
|


|